Quality, that shapes!
FAQ
Marking Method
We will explain to you which methods can be used. Our aim is to provide you with the essential information to make informed decisions. If you have any further questions, please do not hesitate to contact us.
Dot Peen Marking Machines
Dot peen marking machines: Everything you need to know
Dot peen marking machines play a central role in modern industry.
They are indispensable for permanently marking materials and products to ensure their
traceability. This article tells you everything you need to know about how they work,
their possible uses and the advantages of these devices, as well as the latest technological
developments.
What are dot peen marking machines?
Definition and function of dot peen marking machines
A dot peen marking machine is a specialised marking machine that uses a stylus to create a small indentation
in a material’s surface. These small marks form a
pattern that can represent numbers, letters or symbols. Dot peen marking machines provide
a permanent and precise method of marking surfaces without relying on paint,
stickers or other techniques that are prone to wear and tear.
Differences to other marking methods
Compared to engraving, laser or etching, dot peen marking offers a robust, deeper marking. Unlike laser marking, which produces a uniform and visually appealing surface marking, dot peen marking is particularly suitable for harsh environments and materials that have to withstand extreme conditions.
Structure and function of dot peen marking machines
The mechanics behind the marking
The way a dot peen marking machine works is impressively simple and yet
effective. A controlled needle moves vertically on the surface and punctures it
precisely at fixed intervals. The depth and frequency of the punctures can be individually adjusted to perfectly adapt the marking to the respective application.
Needle drive type
The needle, which is either made of solid hard metal (longer service life) or has a hard metal insert, can be driven by a magnet or compressed air. Although compressed air is stronger and can therefore make a deeper impression, it is also a more expensive medium than electricity and significantly louder.
Software for dot peen marking systems
Many dot peen marking machines are equipped with specialised software that allows users to programme custom designs and marking patterns. Such software solutions make it possible to flexibly customise and save font sizes, layouts and various marking types.
Digital control and precision
Modern dot peen marking machines can be digitally controlled by a host system, enabling impressive accuracy and flexibility. With computer control, the marking can be precisely positioned and the desired data – such as serial numbers or production codes – can be stamped into the material in a few seconds.
Applications for dot peen markers
Dot peen markers in the automotive industry
In the automotive industry, dot peen marking is crucial for traceability and quality control. Serial numbers and production data are marked on vehicle parts, enabling seamless tracking along the entire supply chain.
Applications in medical technology
In medical technology, precise and permanent marking is essential. Dot peen markers
are used on surgical instruments and medical devices to visibly and permanently store important information such as the manufacturing date and serial number.
Use in the metal and machine industry
The metal and engineering industries rely on dot peen marking to identify
machine parts and tools. These marks are robust and withstand high temperatures, humidity and other extreme conditions.
Electronics and micro engineering
Dot peen marking is also being used more and more in the electronics industry. Its small size and ability to precisely mark small components make it ideal for micro engineering applications such as labelling circuit boards.
Benefits of dot peen marking machines
Permanent markings for maximum traceability
Dot peen markings are deep and permanent, making them perfect for traceability. Even in harsh environmental conditions, the marking will remain and can be read throughout the lifetime of a product.
Robustness in challenging environments
Dot peen marking can withstand extreme conditions, whether it be heat, humidity or heavy use. This durability makes dot peen marking machines a top choice in heavy industries where traditional marking methods may fail.
Flexibility and customisability
Dot peen marking machines are highly customisable and can be tailored to suit different materials and marking requirements. Whether it be fine text or large numbers, the configuration can be easily changed to achieve the desired results.
Challenges and potential limitations
Noise and sound
One disadvantage of dot peen marking machines is the noise, as the stylus marking motion produces sound. In quiet working environments, this can be disruptive and protective measures may be required to reduce the impact on staff.
Limited application on certain materials
While dot peen markers can be used on many materials, there are some limitations. Soft and delicate materials could be damaged by the marking action, making dot peen marking machines less suitable in such cases.
Selecting the right dot peening machine
Criteria for selection
The choice of the right machine depends on various factors: the material to be marked, the requirements for the depth of the marking and the desired speed. It is also important to consider additional features such as software compatibility and ease of maintenance.
Maintenance and lifespan
Regular maintenance of the dot peening machine is necessary to extend its lifespan and ensure consistent marking quality. This includes cleaning and, if necessary, re-sharpening or replacing the styli to ensure functionality.
The future of stylus marking technology
Technological innovations and automation
Stylus marking technology continues to evolve. Automation and digitalisation enable the integration of dot peen marking machines into fully automated production lines. In the future, AI-powered systems could further increase the efficiency and precision of these machines.
Conclusion
Dot peen marking machines are essential tools in numerous industries. With their robust and durable markings, they provide an excellent solution for traceability and product safety. Despite some minor limitations, they remain unbeatable for industrial applications and are becoming even more powerful thanks to new technologies.
FAQs
What is the main advantage of a dot peen marker?
The biggest advantage of dot peen markers is their ability to create durable and extremely robust marks that remain legible in adverse conditions such as high heat, humidity and wear. This makes them ideal for applications that require high traceability.
What materials can be marked with dot peen markers?
Dot peen marking machines are suitable for a wide range of materials, including metals such as
stainless steel, aluminium and titanium, as well as harder plastics. However, they are limited when it comes to very soft or brittle materials, as the marking action could cause damage to the mark.
Are dot peen marking machines capable of small and intricate designs?
Yes, dot peen marking machines can be highly accurate and are therefore able to apply small and detailed markings. In industries such as electronics, they are used to apply legible and permanent markings in limited spaces, such as on tiny components.
Is special software required to operate them?
Many modern dot peen marking machines offer the option of controlling them via software and customising individual markings. The software makes it easier to create and customise markings by making the layout, font size and design programmable according to the user’s wishes.
How loud are dot peen marking machines when in operation?
Dot peening machines can be relatively noisy in operation because the needle makes contact with the material mechanically. In work environments where noise is an issue, sound-absorbing measures or the use of special work areas may be necessary to reduce the impact on personnel.
This detailed overview gives you a comprehensive insight into the world of dot peen markers. The technology behind these devices is constantly evolving to provide greater precision, flexibility and the ability to integrate into modern production processes. If you are looking for a robust, long-lasting and adaptable marking solution, dot peen marking machines could be just right for your requirements.
Scribe Marking Machines
Scribe Marking – precise, durable and robust marking for industry
Scribers have become an indispensable tool in modern industry, especially when it comes to permanent and precise marking on metals and other hard surfaces. The technique of scribing offers many advantages over traditional engraving methods and is particularly valued in industries such as automotive, aerospace and medical technology. This article provides a comprehensive insight into how scribing technology works, how it can be used and its advantages.
What is a scribe marking machine?
How a scribe marking machine works
The scribing process is achieved by a hard tip that is pressed against the surface under high pressure. This pressure ensures that a permanent indentation is scribed into the material without significantly deforming it.
The technique of scribing instead of engraving
In contrast to engraving, scribing does not remove material but displaces it, resulting in a more robust marking. This method ensures a particularly deep and legible marking that can withstand extreme conditions.
Applications of scribers
Automotive
In the automotive industry, scribers are used to mark parts such as engines and body panels. These marks are important for identification and traceability throughout the production chain.
Aerospace
Material strength and reliability requirements are particularly high in the aerospace industry, making scribing the preferred marking method for parts such as metal structures and components.
Advantages in aviation
The scribing technique makes it possible to apply markings that can withstand extreme temperatures and stresses, which is a crucial safety aspect in aviation.
Other areas of application
Scribers are also used in medical technology and in the manufacture of tools and metal parts. They provide a durable and reliable solution for permanently marking products.
Advantages of scribers
Permanent and precise marking
A key advantage is the durability of the marking. The scribing process leaves a deep indentation that remains clearly legible even under extreme conditions.
No impairment of the material
By displacing rather than removing material, the structure of the material is less affected, which is particularly important for safety-related parts.
Differences between scribing and engraving
While engraving removes material, scribing only creates an indentation that displaces the material. Both methods have advantages and disadvantages depending on the application.
Accuracy and speed
Scribers offer high precision and often require less time than engraving methods, making them particularly attractive for serial production.
Influence on material structure
By displacing material instead of removing it, the integrity of the material is largely preserved.
Technical properties and performance criteria
Compressive force and hardness
The strength and hardness of the tip of a scriber determine how deep the mark will be and which materials can be processed. Special, robust tips are required for particularly hard metals.
Wear and maintenance requirements
Regular maintenance and occasional tip replacement will extend the lifespan of the device and ensure consistent marking quality.
Tips for choosing the right scriber
There are various models and features to consider when choosing a scriber.
Industry-specific requirements
The aviation industry requires robust devices with high printing force, while a standard model may be sufficient for simpler applications.
Durability and maintenance costs
It is important to consider the lifespan and maintenance costs to ensure a cost-effective solution in the long term.
Conclusion
Scribers are a valuable investment for companies that require durable and resilient markings. Their robustness, durability and precision make them the ideal choice for demanding industrial environments.
FAQs:
What is the difference between scribing and engraving?
Scoring displaces material, rather than removes it, which makes for a particularly deep and consistent mark. Engraving, on the other hand, removes material and is often used for more precise, but shallower, marks.
What materials can a scriber mark?
Scribers can be used on hard materials such as stainless steel, aluminium, titanium and other metals. They are ideal for materials that require particularly durable marks.
What are the main industries that use scribers?
The main industries are automotive, aerospace and medical, where permanent marking is essential to ensure identification and safety standards.
What are the advantages of scribing over other marking methods?
Scribing produces a permanent and resilient mark that is less susceptible to abrasion. It also preserves the material structure because the material is only displaced and not removed.
How do I maintain my scriber to ensure a long service life?
Regular maintenance is important, especially checking and replacing the scriber tip if necessary. Cleaning and inspecting the mechanical parts can help maintain performance and precision over a long period of time.
Laser Marking Systems
Laser marking systems: Everything you need to know
Laser marking systems are the perfect solution for precise, permanent and fast marking of a wide variety of materials. Whether it’s serial numbers, logos, or QR/DMC codes, lasers ensure that the marking is resistant to abrasion and environmental conditions. In this article, you will learn everything about how laser marking systems work, the different types and applications, and how to find the right system for your needs.
What are laser marking systems?
Definition and how they work
A laser marking system uses a high-energy laser beam to permanently mark the surface of a material. The laser beam heats or changes the material with pinpoint accuracy to create precise lettering, codes or graphics. Depending on the type of laser, the marking can be done by engraving, discolouration or colour change without damaging the material.
Differences to conventional labelling methods
Laser marking systems offer greater durability and precision than conventional methods such as printing or etching. In addition, no ink or chemicals are required, which makes laser marking particularly environmentally friendly and low-maintenance.
Structure and types of laser marking systems
Fibre lasers
Fibre lasers are ideal for marking metals and hard plastics. They are characterised by their high beam quality and efficiency. Fibre lasers are particularly popular in the automotive and mechanical engineering industries due to their robustness and high marking speed.
CO₂ lasers
CO₂ lasers are excellent for marking non-metallic materials such as glass, cardboard, wood and textiles. This type of laser is frequently used in the packaging industry and for processing organic materials.
UV laser
UV lasers are ideal for materials that are sensitive to high temperatures. The ‘cold’ laser process results in precise markings without heat damage. UV lasers are often used in electronics and medical technology, where particularly gentle treatment is necessary.
Other types of laser and their special features
In addition to the common types of laser, there are also green lasers and ultrashort pulse lasers. These special lasers are ideal for applications that require even greater precision and gentler treatment of materials, for example, with delicate surfaces or surfaces that are difficult to mark.
Areas of application for laser marking systems
Automotive industry
The automotive industry uses laser marking for part IDs, serial numbers and barcodes to ensure traceability. Lasers are unbeatable here in their ability to create even the smallest and most durable markings on metal and plastic.
Electronics and microtechnology
In the field of electronics, where components are often tiny, lasers offer the possibility of applying precise markings in the smallest of spaces. They are used to mark chips, printed circuit boards and sensors.
Medical and pharmaceutical
In medical technology, lasers are indispensable for making instruments and devices traceable. Laser marking ensures hygiene and durability, as it is resistant to sterilisation and cleaning.
Aerospace
The aerospace industry requires strict labelling standards. Lasers can apply high-quality markings to durable materials such as titanium and aluminium, helping to meet safety and traceability requirements.
Jewellery and luxury goods
Lasers are used in the jewellery and luxury goods industry to create individual engravings without damaging the precious material. Here, the laser offers the possibility of setting extremely delicate and detailed markings.
Advantages of laser marking systems
Precision and durability
Lasers offer impressive precision and the markings are so robust that they resist wear, UV light and chemicals. They are ideal when permanent and precise markings are required.
Environmental friendliness and safety
Since laser marking does not require consumables such as ink or chemicals, it is an environmentally friendly alternative. The processes are clean and safe and produce less waste.
Flexibility and adaptability
Laser marking systems are adaptable and easy to integrate into automated manufacturing processes. A wide range of materials can be marked with little effort, which increases flexibility.
Disadvantages and challenges
Costs and maintenance
The initial costs for laser marking systems are higher than for conventional marking methods. Although maintenance is manageable, repairs and replacement parts can be costly.
Material restrictions
Laser marking is not ideal for all materials. Transparent or reflective surfaces pose a challenge and require special lasers or additional pre-treatment of the material.
Selecting the right laser marking system
Requirements and materials
When choosing a laser system, you should consider the material to be processed and the type of marking you want. Metal, wood or glass require different types of lasers for optimal results.
Efficiency and energy consumption
Efficiency and power consumption vary between laser types. While fibre lasers are energy efficient, CO₂ lasers require more energy. A precise analysis of requirements will help you decide on the appropriate system.
The future of laser marking technology
Innovation and automation
Laser marking technology is constantly evolving. Fully automated systems that integrate seamlessly into production lines are becoming more prevalent. Artificial intelligence and improved control systems are making laser markings faster and more precise.
Sustainable developments
The future of laser marking is also sustainable. New developments are aimed at further reducing energy consumption and minimising environmental impact. Manufacturers are seeking innovative ways to maximise the lifespan and efficiency of lasers.
The bottom line
Laser marking systems provide a precise, robust and environmentally friendly solution for marking a wide range of materials. They are particularly suited to industries where quality and traceability are paramount. Despite high initial costs and specialised material requirements, advanced technologies and adaptability make them a future-proof investment.
FAQs:
Why are laser marking systems environmentally friendly?
Laser marking systems do not use inks or chemicals, which minimises waste and the use of harmful substances. They also use less energy than many conventional marking methods, thus conserving resources.
What materials can be marked using a laser marking system?
Laser marking systems can mark a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, glass, wood and ceramics. However, some types of laser, such as CO₂ lasers, are more suitable for organic materials, while fibre lasers are ideal for metals and plastics.
How long do laser marking system markings last?
Laser marking system markings are permanent and can even withstand extreme conditions such as abrasion, high heat and UV radiation. This makes them ideal for industrial applications where long-term legibility is required.
Are laser marking systems safe to operate?
Yes, laser marking systems are safe to operate provided the necessary protective measures are followed. Most modern laser devices have protective devices that prevent direct contact with the laser beam. Safety at work is further enhanced by protective enclosures and goggles.
What role does software play in laser marking systems?
The software controls the entire marking process and makes it easy to design and customise markings. From font size to alignment, everything can be digitally adjusted. Advanced software often also offers the option of integration into automated production systems, which increases efficiency and expands marking options.
This comprehensive introduction to laser marking systems shows how versatile, efficient and sustainable this technology is in modern production processes. Whether for industrial or specialised applications – laser marking systems offer precision and durability at the highest level.
Mobile Inkjet Printer
Mobile inkjet printers: everything you need to know about Handjet, Jetstamp and co.
Mobile inkjet printers offer a versatile, flexible solution for modern production and shipping processes. They enable fast and precise printing directly on the spot – perfect for small businesses, warehouses or mobile applications. No more hassle transporting products to the printer – mobile printing devices like the Handjet and Jetstamp make life easier in industry and logistics.
What are mobile inkjet printers?
Overview of how they work and their advantages
Mobile inkjet printers work in a similar way to traditional inkjet printers, but are so compact that they can be held in the hand. They use ink that is applied to the desired material by pressure, often in a resolution that is sufficient for logos, text or barcodes. They are easy to use and the results – razor-sharp prints on a wide variety of surfaces – are impressive.
Main applications for mobile inkjet printers
Whether it’s boxes in the warehouse, wooden crates, pipes or packages, mobile inkjet printers can print on almost any surface. They are particularly useful in logistics, product labelling, packaging and warehousing. With fast printing and versatile options for materials, they make labelling easier wherever flexibility is required.
The most popular models at a glance
The Handjet: Flexibility and speed
The Handjet is a popular mobile inkjet printer, known for its ease of use and high print speed. With an ergonomic design, it is ideal for continuous use. It also offers impressive battery life and fast ink drying time, making it an excellent choice for a wide range of applications.
The Jetstamp: efficient and precise
The Jetstamp is another top model in the mobile printing sector. It impresses with high printing precision and is ideally suited for fine and detailed labelling. Whether barcodes, serial numbers or QR codes – the Jetstamp delivers high-quality results, even on difficult surfaces.
Advantages of mobile inkjet printers over stationary models
Mobility and flexibility
Mobile inkjet printers can be used anywhere. Unlike stationary models, they are not tied to a fixed location, which is particularly helpful in the logistics industry. The ability to print directly on the product saves time and increases efficiency.
Can be used on a variety of materials
Versatility is a clear plus: mobile inkjet printers can print on wood, metal, plastic, cardboard and glass. This flexibility makes them the first choice for companies that need to print on a variety of surfaces.
Speed and efficiency in practice
Mobile inkjet printing enables fast work without having to bring the product to the printer. A quick press of a button and the printing is done – faster than with traditional methods and perfect for high throughput rates.
Technical specifications and functions of mobile inkjet printers
Print quality and resolution
High-quality models offer print resolutions of up to 600 dpi, which is more than sufficient for most applications. The sharpness of the print image remains constant on different surfaces.
Battery life and charging options
Mobile inkjet printers are equipped with powerful batteries that are designed for several hours of operation. Many models can be charged via USB or special charging stations, so they can last through long work shifts.
Connectivity and compatibility
Many mobile inkjet printers today are Bluetooth or Wi-Fi compatible, enabling wireless printing. This makes it easy to connect them to laptops, tablets or smartphones, making the printing process even faster and less complicated.
Tips for using mobile printers
Maintenance and care for a long service life
To ensure that the printer gives you good service for a long time, regular cleaning is important. The print nozzle should be kept clean to maintain print quality. Also, be careful not to discharge the battery completely and store the printer in a safe place when not in use.
Optimising print quality
Choosing the right ink and the appropriate resolution is crucial for the print result. If necessary, test prints can help you find the optimal settings. Avoid excessive moisture and dirt on the surface to be printed on to achieve an even print image.
Make the right choice: Handjet or Jetstamp?
Which criteria are important when making your selection
Consider what you need from the printer. The Handjet is suitable for quick and flexible applications, while the Jetstamp is preferred for more precise printing. To make the right choice, also consider the material and size of the surfaces you want to print on.
Costs and availability
The cost of mobile inkjet printers varies greatly. Simple models are available from around €800, while more powerful devices with more features can cost up to €3,500. Depending on your needs, investing in a more expensive model can save time and effort in the long term.
Conclusion
Mobile inkjet printers are a worthwhile investment for companies that require flexibility and efficiency when printing on a wide range of materials. Whether it’s the Handjet for quick jobs or the Jetstamp for precise labelling, these printers offer a suitable solution for almost every need. In today’s world, where speed and adaptability are required, mobile inkjet printers are a reliable partner in everyday life.
FAQs:
What surfaces can a portable inkjet printer print on?
Portable inkjet printers can print on a variety of surfaces, including metal, plastic, wood, cardboard and glass. Make sure you choose the right ink for the material.
How long does the battery of a portable inkjet printer last?
Battery life varies depending on the model. On average, mobile inkjet printers can be used for several hours before they need to be charged.
Can I control the printer with a smartphone?
Yes, many mobile inkjet printers are Bluetooth-compatible and can be connected to smartphones or tablets, making printing even easier.
Is a mobile inkjet printer suitable for large production volumes?
Mobile printers are well suited for small and medium-sized production runs. However, for very large volumes, a stationary printer may be more suitable. Stationary inkjet printers often have a higher print speed and can be operated continuously for extended periods. Mobile printers are ideal for flexible applications and small to medium-sized production runs where it is important to quickly apply the print to different locations.
What types of ink are available for mobile inkjet printers?
There are various types of ink for mobile inkjet printers, including water-based inks, UV inks and solvent inks. The choice of ink depends on the material and the desired print properties. Solvent inks, for example, are more weather resistant and adhere well to smooth surfaces, while water-based inks are more environmentally friendly.
Pneumatic-Hydraulic Embossing Presses.
Pneumatic-hydraulic marking presses: efficient power for precise markings
Pneumatic-hydraulic marking presses combine the advantages of pneumatic and hydraulic systems to enable high-performance and precise marking on a wide variety of materials. They provide an efficient solution for industrial production where strong and durable markings are essential. In this article, you will learn how pneumatic-hydraulic marking presses work, where they are used and what advantages they can offer companies.
What is a pneumatic-hydraulic marking press?
How pneumatic-hydraulic marking presses work
A pneumatic-hydraulic stamping press uses a pneumatic drive to generate a hydraulic pressure force. This combination ensures that the press can work both quickly and with high forces. The pneumatic part generates the initial pressure, while the hydraulic system amplifies this pressure and thus delivers the force required for precise and deep embossing.
Distinction from other stamping presses
Compared to purely pneumatic or hydraulic presses, pneumo-hydraulic presses offer greater energy efficiency and flexibility. Purely hydraulic systems often deliver higher forces, but are slower and require more maintenance. In addition, a lot of oil must be stored. Pneumatic systems, on the other hand, are fast, but do not achieve the same compressive force and ‘hit’ the material. The pneumo-hydraulic combination is therefore particularly efficient for industrial applications.
Components of a pneumatic-hydraulic stamping press
Pneumatic system
The pneumatic system is responsible for the initial movement of the piston. By using compressed air, the piston is activated and then passes into the hydraulic cylinder, transferring the stamping force to the material. This method reduces energy consumption, since air is cheaper and easier to handle.
Hydraulic cylinder and its role
The hydraulic cylinder is responsible for the decisive pressure build-up to create the embossing in the material. It ensures that the force is transferred to the workpiece in a constant and controlled manner. This is particularly important for materials that require consistent and deep embossing.
Control and precision mechanisms
Modern pneumo-hydraulic marking presses are equipped with control elements and precision mechanisms that allow flexible adjustment of the marking parameters. This means that the press force can be precisely regulated to mark different materials without damage or deviations.
Applications of pneumo-hydraulic marking presses
Automotive industry
Pneumo-hydraulic marking presses are indispensable in the automotive industry. They are used to mark components and body parts with serial numbers and other information. The machines are ideal for applying robust and durable markings that have to withstand the harsh conditions inside a vehicle.
Metal processing and mechanical engineering
Metal processing requires precise and deep markings. Pneumatic-hydraulic marking presses offer a powerful and reliable solution for applying permanent markings to steel and other metals that remain legible for years.
Electronic manufacturing
The electronics industry requires particularly compact embossing presses that can be used on small components or printed circuit boards. The precise pressure control of pneumatically-hydraulic presses enables clean and long-lasting labelling without damaging sensitive electronic components.
Medical technology and pharmaceutical industry
Durable and precise markings are also important in the medical and pharmaceutical sectors, for example on devices and instruments that need to be sterilised. Pneumo-hydraulic marking presses are particularly suitable here, as they apply stable and durable markings without distortion or contamination.
Advantages of pneumo-hydraulic marking presses
High precision at reduced costs
The combination of pneumatics and hydraulics enables precise control of the stamping force, resulting in clean and detailed markings. At the same time, energy consumption is lower, which can reduce operating costs.
Powerful markings with lower energy consumption
Pneumo-hydraulic marking presses are highly energy efficient. They use the pneumatic energy for the majority of the operation and only activate the hydraulics when the highest force is required. This saves resources and reduces operating costs.
Maintenance-friendly and durable
The simple design and robust construction mean that pneumo-hydraulic coining presses require little maintenance and have a long service life. They are designed to work reliably for many years, even in demanding applications. Maintenance is usually straightforward, which makes the machines particularly attractive for continuous use.
Challenges and limitations
Limited flexibility in materials
Pneumatic presses are suitable for many materials, but not all. Very soft or brittle materials can be damaged by the high compressive force. This makes them particularly suitable for harder materials such as metals and hard plastics.
Initial investment and maintenance costs
The purchase of a pneumatic-hydraulic stamping press is often cost-intensive. Although the running costs are low, maintenance and spare part costs may be incurred. A thorough cost-benefit analysis is therefore recommended.
Selecting the appropriate pneumatic-hydraulic stamping press
Criteria for selection
When choosing a pneumatic-hydraulic marking press, aspects such as the required marking force, the control elements and the compatibility with the materials to be processed should be taken into account. The selection depends heavily on the specific application and the marking requirements.
Possible uses and required force
The required pressure can vary depending on the material and marking depth. Harder materials require higher pressure, which only certain marking presses can deliver. The press should therefore always be matched to the specific application.
Innovations and the future of pneumo-hydraulic marking presses
Automation and Industry 4.0
The integration of pneumatic-hydraulic coining presses into automated production lines is already widespread today and is being further advanced by Industry 4.0. Modern presses can be integrated into digital networks via software control. This enables a quick adjustment of the coining parameters, making production more flexible and efficient. Integration into production systems also offers the possibility of continuously monitoring and optimising the coining processes. Automated systems
not only increase productivity, but also the accuracy of the embossing – perfectly meeting the requirements of modern industry.
Environmentally friendly developments
Sustainability is also becoming increasingly important in the field of pneumo-hydraulic embossing presses. Newer models are being developed to work even more energy-efficiently and to use materials in a resource-saving way. In addition, some manufacturers are working on recyclable components and environmentally friendly production to further reduce their environmental footprint. The future lies in durable machines that
conserve resources and are energy efficient – a clear advantage for companies that value sustainability.
Conclusion
In summary, pneumatic-hydraulic marking presses are a reliable and efficient solution for companies that require permanent and precise markings. By combining pneumatics and hydraulics, they provide an ideal blend of power and speed, making them suitable for numerous industrial applications. The constant advancement of this technology, particularly in the areas of automation and sustainability, makes it a future-proof investment. Whether in the automotive industry, metal processing or medical technology – pneumo-hydraulic marking presses are indispensable tools that can take the production process to a new level.
FAQs:
How does a pneumatic-hydraulic coining press work?
A pneumatic-hydraulic coining press combines pneumatic (air pressure) and hydraulic (fluid pressure) systems. The pneumatic part initiates the movement of the piston, while the hydraulic cylinder amplifies the pressure and provides the force needed for coining.
What are the advantages of pneumatic-hydraulic coining presses?
Pneumatic-hydraulic marking presses are powerful, precise and energy-efficient. They enable permanent marking with lower energy consumption and are easy to maintain, which makes them particularly economical.
In which industries are pneumatic-hydraulic marking presses used?
These marking presses are used in the automotive industry, in mechanical engineering, in electronics manufacturing and also in medical technology. They are particularly suitable for industries where permanent and precise labelling is required.
What materials can be embossed?
Pneumo-hydraulic marking presses are particularly suitable for hard materials such as metals and plastics. However, they are less suitable for very soft or brittle materials that could be damaged by the high pressure force.
How future-proof are pneumo-hydraulic marking presses?
Pneumo-hydraulic presses are very future-proof thanks to their ability to be integrated into automated production lines and the ongoing development of more environmentally friendly models. The continuous optimisation of this technology ensures that it will also meet future production requirements.
Spring-loaded and Toggle Presses
Spring-loaded and toggle presses: everything you need to know
Spring-loaded impact presses and knuckle-joint presses are mechanical machines that are frequently used in metalworking, embossing and punching. Both types have their particular advantages, and the choice often depends on the type of application. While spring-loaded impact presses are preferred for faster embossing processes, knuckle-joint presses offer more precision and even power transmission, e.g. for hot stamping.
How spring-loaded presses work
Structure and principle of the spring-loaded press
Spring impact presses use the force of a tensioned spring to strike the workpiece with high speed and intensity. They are simple in design, efficient and require relatively little maintenance, as they usually work without additional energy sources. These machines work quickly and are suitable for many smaller punching and stamping applications.
Areas of application for spring-loaded presses
Spring impact presses are widely used in the production of metal parts, in the manufacture of coins or medals, and in the jewellery industry. Thanks to their speed and ease of use, they are a popular choice for processes that do not require extreme precision but do demand a high level of efficiency.
How toggle presses work
Structure and principle of the toggle press
Toggle presses work by using a lever system that allows for smooth and controlled force transfer onto the workpiece. These presses feature a very precise and powerful motion that is particularly useful when forming and punching thicker or harder materials.
Typical applications of the toggle press
Toggle presses are often used in the automotive industry, in the manufacture of heavy machinery or in areas where high precision and strong press force are required. Thanks to their controlled movement, they are well suited for delicate or detailed work, such as hot stamping or joining components.
Comparison of spring-operated and toggle presses
Advantages and disadvantages of both press types
Both types of press have their advantages. While spring-loaded presses are faster and easier to operate, knuckle-joint presses offer more precision and consistency in the pressing force. When it comes to high accuracy, the knuckle-joint press has the advantage. For high volumes of less delicate materials, however, spring-loaded presses score higher.
Energy consumption and efficiency
Spring-operated impact presses generally do not require an external energy source and are therefore often more cost-effective to operate. In contrast, knuckle-joint presses can require more energy, but are more efficient for demanding applications.
Precision and force transmission
Toggle presses are the best when it comes to controlled force and high precision. The force is applied evenly, so they ensure precise and high-quality results. Spring-loaded impact presses, on the other hand, provide a fast, impulsive force application and are therefore well suited for simple and quick stamping operations.
Tips for using spring-loaded and toggle presses
Maintenance and care
To ensure that spring-action and toggle presses work reliably, they should be serviced regularly. For spring-action presses, it is important to check the springs for tension and wear. For toggle presses, the maintenance of the lever system is crucial to ensure even power transmission. Both types benefit from regular cleaning and inspection.
Safety instructions
Operating these presses requires a trained eye and an awareness of safety hazards. Always wear eye protection to prevent injury. Make sure to regularly inspect moving parts and keep all safety devices in good working order.
Choose the right press for your application
Important purchase criteria
Consider what your requirements are for the press. Is it more about speed or precision? Spring-loaded presses are ideal for simple and quick jobs, while toggle presses are better for precise and more demanding tasks. The size and weight of the workpiece also play a role in choosing the right press.
Costs and cost factors
The cost depends heavily on the type of press and its capacity. Spring-action presses are often cheaper and require less maintenance, while toggle presses are usually more expensive, but offer greater long-term efficiency and quality for more complex tasks. Additional features such as electronic control and
safety devices can also affect costs.
Conclusion
Spring-loaded and toggle presses offer unique advantages for different applications. While spring-loaded presses score points for speed and efficiency, toggle presses are particularly suitable for precise and demanding work. The right choice depends on your specific requirements – so think carefully about what you need to get the most out of your machine in the long term.
FAQs:
What is the main difference between spring-loaded and toggle presses?
The biggest difference is the way force is applied. Spring-loaded presses use a fast, impulsive force from a spring, while toggle presses provide a smooth and precise force from a lever system.
Which press is more durable?
Both presses are durable when well maintained. However, knuckle joint presses tend to last longer in demanding applications because they are better designed to perform consistently and accurately.
Are spring-loaded presses or knuckle joint presses more maintenance-intensive?
Toggle presses require more frequent inspections of the lever system, while spring-loaded presses require less maintenance as long as the spring is intact.
Which press is better for precision work?
Toggle presses are better suited for precise work due to their even force transmission. Spring-loaded presses, on the other hand, are suitable for faster, less precise applications.
Can I use both press types for metal stamping?
Yes, both types of press are suitable for metal stamping. However, the choice of press depends on the precision and speed required. The spring-action press is ideal for fast serial production, while the knuckle-joint press is suitable for detailed and precise stamping.
Embossing Tools
Embossing stamps, embossing tools and embossing machines: The ultimate guide
Embossing stamps and embossing tools are indispensable aids for permanent labelling and finishing of materials. They are used to create texts, logos, structures or patterns on surfaces. Whether in industrial production or in arts and crafts – embossing stamps give materials a distinctive character.
Important differences between embossing stamps and embossing machines
Hand stamps are typically tools used manually or with machines and have fixed texts. There are also so-called type holders that can be used with interchangeable pins, the steel types, to adjust the embossed text. Marking heads, on the other hand, are more complex systems designed for mass production and offer automatic serial numbering, for example.
Different types of hand stamps and marking heads
Hand stamps vs. machine stamps
Hand stamps are ideal for smaller, detailed work, while machine stamps process larger projects automatically. Machine stamps are usually more precise and efficient for high-volume production.
Industrial embossing presses
Industrial embossing presses work with high precision and are often integrated into production lines to emboss high quantities with consistent quality. They are used, for example, in the packaging and automotive industries.
Artistic embossing tools
Special embossing tools are available for art and design that allow artists to emboss fine structures or relief-like patterns on materials such as paper, leather or fabric.
How do embossing stamps and presses work?
The embossing process in detail
During the embossing process, the material is fixed between an embossing stamp and a counter mould and deformed by pressure. This creates a permanent embossing on the surface of the material. The force required for this is applied by means of a hammer, embossing press or automatic punching press.
How the material influences the embossing
The way that material is embossed can vary depending on the material. Harder materials, such as metal, require higher stamping forces and specialised dies, while softer materials, such as leather or paper, can be embossed more easily.
Advantages of embossing tools and mechanisms
Precision and repeatability
Embossing dies and mechanisms offer a high degree of repeatability, enabling even the smallest details to be precisely embossed multiple times – a significant advantage over manually produced embossing.
Functional and aesthetic results
Embossing dies are not only used for practical purposes, such as labelling products, but also to create aesthetic effects. The embossing gives the material a tactile, high-quality feel that is often better perceived than a simple print.
Materials and production of embossing stamps
Types of metal for embossing stamps
Typical materials for embossing stamps are hardened tool steels. These metals are tough and can withstand high pressures without deforming. However, embossing stamps can also be made of brass if they are used for hot stamping, for example. Since more and more high-strength steels are being used in automotive engineering, powder-metallurgical steels are also being used more and more. In addition, there are special steels for hot stamping at over 800°C, e.g. for railway wheels.
Manufacturing techniques: engraving, etching, eroding and cold forming
Methods such as engraving, eroding, etching or cold forming are used to produce an embossing die. Engraving, eroding and etching allow for very fine details, while cold forming is used primarily for larger series to save time and money. However, cold forming also results in a shorter lifespan for the stamp, which is why this method is not used by Röltgen.
Applications of marking tools and marking units
Packaging industry
Marking tools are widely used in the packaging industry to mark product packaging with expiry dates and batch numbers. The graphic design on cardboard packaging can also be enhanced by means of embossing.
Automotive and mechanical engineering industry
The automotive and engineering industries frequently use embossing to mark and identify components. This ensures that serial numbers or manufacturing information remains permanently visible.
Jewellery and design
In the world of jewellery and design, embossing is used to create artistic effects. Designers use embossing tools to apply three-dimensional textures to various materials, thereby creating unique works of art.
Tips for choosing the right embossing tool
What to look for when choosing a material
The choice of material is crucial: for hard materials, hardened steel is optimal, while brass is ideal for embossing (cold or hot) on softer materials such as leather. To ensure a long service life, make sure that the material of the stamp is suitable for the desired application.
Important: Customisability and maintenance requirements
The flexibility of an embossing tool is also important. Some tools offer interchangeable character sets (e.g. A-Z or 0-9) or variable adjustment options (embossing wheels on an embossing tool) to change the embossing. In addition, the tool should be easy to clean, as this increases its lifespan.
Care and maintenance of marking tools
A marking stamp or marking tool will only remain functional for a long time if it is regularly maintained and cleaned. Remove dust and material residues after each use with a soft brass brush and take care not to damage the marking surfaces. Regular oiling of moving parts can also be useful.
Conclusion:
embossing stamps and embossing presses are indispensable tools in a variety of industries. They enable precise, high-quality and permanent embossing that fulfils both functional and aesthetic purposes. From the packaging industry to the automotive industry and jewellery and design – embossing tools offer countless possibilities for uniquely refining materials and marking them for the long term.
FAQs:
Which materials can be embossed?
Typical materials for embossing are paper, leather, fabrics, plastic and metal. However, each material requires a specific embossing tool.
What is the difference between etching, eroding and engraving in embossing production?
In etching, the surface is removed chemically and in eroding, electrically to create the engraving, while in engraving, the material is removed mechanically.
How deep can an embossing be?
The depth of the embossing depends on the material and the embossing tool, but is typically between 0.1 and 1 mm and can be even deeper for special applications. For decorative purposes on soft materials such as leather or paper, a shallow depth is sufficient, while industrial embossing on metal often requires a deeper engraving to remain visible even under heavy use.
How long does an embossing stamp last?
The lifespan of an embossing stamp depends on the material it is made of, how it is cared for and how intensively it is used. High-quality embossing stamps made of hardened steel or brass can last for many years with good maintenance. However, use on hard materials or with high pressure can accelerate wear and tear, so regular inspections and care are advisable.
Technical questions
Do you have technical questions about embossed printing, engraving, etc.? Then you’ve come to the right place. However, you are also welcome to receive a personal consultation on site. Just get in touch.
What is a data matrix code or DMC?
Introduction to the Data Matrix code
The Data Matrix code is an indispensable tool for collecting and tracking data today. But what exactly is it, and why is this small, often square code so important? This article provides a comprehensive overview of the Data Matrix code: how it works, its applications, advantages, and how it could become even more important in the future.
Definition and origin of the Data Matrix code
The Data Matrix code is a two-dimensional barcode that stores information in a compact, square grid. Developed in the 1980s, it quickly found applications in industry, where its ability to store a large amount of data in a small space was appreciated. Unlike traditional barcodes, the Data Matrix code uses a matrix structure of light and dark dots arranged vertically and horizontally to encode information.
The difference to other code systems
While barcodes store data in only one direction, the Data Matrix code, with its two-dimensional structure, allows for a greater density of information in a smaller area. QR codes and data matrix codes may look similar at first glance, but there are clear differences: the data matrix code is specially designed for tiny areas and is therefore ideal for labelling small parts, for example in the pharmaceutical industry or electronics.
Structure and function of the data matrix code
Structure and design
A Data Matrix code consists of a matrix in which small, square cells (modules) are either light or dark in colour. These patterns represent binary data that scanners and readers can decode. A characteristic feature is the ‘L-shaped’ recognition mark on two edges of the code, which provides orientation during scanning and helps to identify the exact orientation of the code.
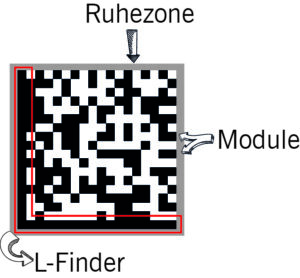
Why is it square?
The square shape of the Data Matrix code is particularly useful because it allows for compact data storage. Unlike elongated barcodes, the Data Matrix code can fit information into a very small space without losing readability.
Advantages of the square shape
The square shape not only ensures a compact size, but also a high data density. Even if parts of the code are damaged or covered, the content often remains legible thanks to special error-correction algorithms.
Technical details: How the code is read
The data matrix code is read using special scanners that decode the binary patterns and convert them into readable information. Modern scanners are able to deliver accurate results even under poor conditions, such as low lighting or an uneven surface. Thanks to the integrated error correction, the data matrix code is often still fully readable even if it is partially damaged.
Areas of application for the data matrix code
Data Matrix codes in industry
Data Matrix codes have long been established in industry. They are used for component labelling, traceability and production chain monitoring. The compact code can be applied to small surfaces such as screws or microprocessors, enabling efficient tracking.

Applications in healthcare
The data matrix code is also an indispensable tool in the healthcare sector. Medications, laboratory samples and medical devices are often labelled with data matrix codes to ensure traceability and safety. In the case of medications in particular, the code helps to prevent counterfeiting and to store important information such as batch numbers and expiry dates.

Transport and logistics
In logistics, the data matrix code plays a central role in tracking and managing the flow of goods. Thanks to its high data density, it can display important information such as product details, serial numbers and destinations in the smallest of spaces. This makes warehouse management and the rapid distribution of goods considerably easier.
Data matrix code in retail
In retail, the data matrix code is used for inventory management and product labelling. It helps to efficiently manage stock and enables quick price and product identification. In the future, it could replace QR codes in certain areas because it is more space-efficient and can store more complex data.
Advantages of the data matrix code
High data density and small size
One of the biggest advantages of the Data Matrix code is its ability to store a high density of data in a tiny space. This feature makes it ideal for applications where space is limited.
Robustness and fault tolerance
The Data Matrix code is equipped with powerful error correction that ensures data is still readable even if the code is damaged or partially obscured. This makes it robust and reliable in environments where damage can occur frequently, such as in the manufacturing industry.
Efficiency and time savings
Because the Data Matrix code is compact and stores a lot of data in a small space, it significantly improves efficiency in data collection. Scanners read the information quickly and can recognise even the smallest codes, speeding up work processes in many industries.
Limitations and challenges
Readability challenges
While Data Matrix offers numerous advantages, it also presents challenges. In environments with inadequate scanning technology or older equipment, readability issues can arise, especially when the code is very small or damaged.
Limited support for older equipment
Another obstacle is that not all readers are designed for the Data Matrix code. Older scanners and systems that can only read linear barcodes need to be upgraded to take full advantage of the Data Matrix code.
The future of the Data Matrix code
Development trends and innovations
The future of the Data Matrix code looks promising. With the increase in automation and the need for accurate traceability systems, the use of the Data Matrix code in industry will continue to grow. Exciting possibilities also exist in the area of digitisation, for example, combining it with blockchain technology for even more secure traceability.
Conclusion
The Data Matrix code is a powerful data tracking and storage tool that has proven extremely useful in a range of industries. Its compact size, robustness and efficiency make it an excellent solution for applications where conventional barcodes reach their limits. Whether in industry, healthcare or logistics, the Data Matrix code is a technology that will continue to play an important role in the future.
FAQs
What is the difference between a data matrix code and a QR code?
While both codes are two-dimensional, the data matrix code is particularly suitable for small areas due to its square shape. In addition, the data matrix code has a higher data density in the smallest of spaces.
Why is the data matrix code preferred in industry?
The industry uses the Data Matrix code because of its compact size and high data density, which enables seamless traceability even on tiny surfaces.
Can the Data Matrix code be read if it is damaged?
Yes, the Data Matrix code has integrated error correction, so even damaged codes often remain readable.
In which industries is the Data Matrix code mainly used?
The Data Matrix code is used primarily in industry, healthcare, logistics and, increasingly, retail.
What does the future hold for the Data Matrix code?
The Data Matrix code is expected to continue to grow in importance as the demand for efficient data capture systems and accurate traceability increases.
Which embossed print do I need for my marking?
The embossed print can be calculated. Below you will find a formula for calculating the required pressure. The decisive factor is how many places are to be embossed in which font height in which material.
So you need to know the number of embossed areas, the font height or its factor (see below) and the strength per mm² of the material to be embossed.
The formula includes a certain safety margin, as the presses should never work at the upper limit. They then wear out more quickly.
Embossing force calculation:
To select the right press or punch, it is important to calculate the required stamping force. This is possible with the following formula:
D = F x Z x ST
D = stamping force in N
F = factor (see table)
Z = tensile strength in N/mm2 of the material to be stamped
ST = number of digits
| Character size in mm | deficit factor |
| 1 | 3,4 |
| 1,5 | 5 |
| 2 | 7 |
| 3 | 10 |
| 4 | 14 |
| 5 | 17 |
| 6 | 20 |
| 7 | 23 |
| 8 | 27 |
| 10 | 32 |
| 12 | 40 |
Example:
Stamping of 6 digits in 5 mm font height in S 355 J0 (1.0553)
D = 17 x 500 x 6 = 51000 N = 51 kN
The press should therefore have a force of at least 51 kN to achieve this stamping in good quality.
What types of engraving are there?
In principle, any font can be engraved. However, the DIN1451 font was developed for better readability. This is also requested by 90% of our customers.
In most cases, the engraving is sharp, i.e. the single-line engraving is pointed. The least embossing pressure is required here. However, it is also possible to execute the engraving in two lines, which is then referred to as a double contour. If the notching effect of the engraving is to be counteracted, the engraving must be rounded or executed in points. This prevents the component from being weakened too much by the engraving.
If you are not sure what you need for your application, please do not hesitate to contact us. We will be happy to help.
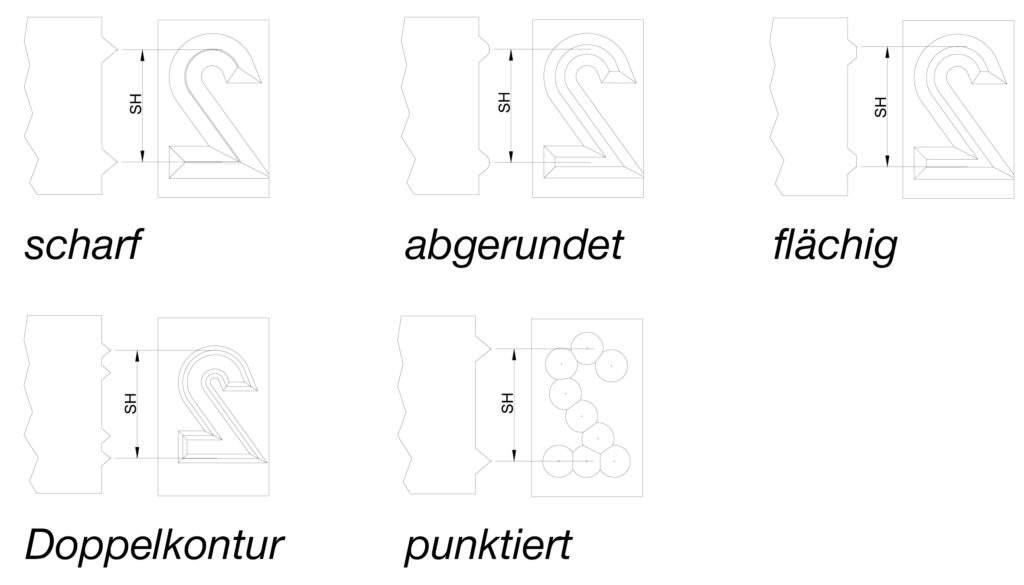
The type of engraving determines the imprint and the embossing force, e.g. a sharp engraving requires less embossing force than a flat one. If a low-stress design is required, a dotted engraving is used.
The character size (SH) is always measured at the highest, outermost point of the engraving. It is best to first press the stamp onto an ink pad and then onto a sheet of paper that is lying on a hard surface. After that, the exact character height can be measured with a vernier caliper.
Which fonts can be used?
In principle, any font can be engraved. However, the DIN1451 font was developed for better readability. This is also requested by our customers in 90% of cases.

DIN 1451 versions:
Fig. above left: DIN 1451-2 narrow
Fig. above right: DIN 1451-3 narrow medium
Fig. below left: DIN 1451-4 medium
Fig. below right: DIN 1451-5 wide
What is the difference between left-hand and right-hand engraving?
The engraving alignment determines whether the imprint is laterally correct or laterally reversed. This must be observed, for example, if the medium is embossed from the back, but the imprint must be legible from the front (e.g. blister packaging) or the marking is embossed in the mould and is to be legible on the cast part afterwards.

Left-hand engraving = imprint legible
Right-hand engraving = imprint not legible
General questions
Here you will find answers to general questions about Röltgen itself and the general framework. If you are unable to find a suitable question or answer, we will be happy to assist you in person.
What sets Röltgen apart from other market players?
For over 80 years, we have been a leading company in the industry. Quality and durability are our top priorities. As a family business, we manufacture marking tools, marking machines, tablet presses and format parts in Germany. Our products are mainly manufactured by our own trained specialists.
Our customers’ satisfaction is our top priority. With a complaint rate of less than 1%, we have earned the trust of well-known companies, from global corporations to hidden champions.
At Röltgen, we are not just colleagues, we are one big family. A friendly working atmosphere and a good work-life balance are important to us.
Our innovative strength drives the market forward. Through close cooperation with renowned universities and research institutes, we are constantly introducing new ideas. Whether it’s the FlexiTab tablet press, the first point marking machine in Germany or hologram embossing on metal as a security feature – our innovations give you a competitive edge.
Sustainability is important to us. With a 120-kW photovoltaic system, LED lighting and a 30,000-litre service water tank, we are committed to environmentally friendly production.
Our first-class customer service extends beyond the point of sale. We offer comprehensive advice, training and on-site repairs.
With Röltgen GmbH & Co. KG, you can count on quality, innovation and excellent customer service. Together, we can achieve your goals.
In which areas does Röltgen provide training?
Röltgen has been providing training for more than 50 years. This is very important to us because it allows us to give something back to society.
We train young people as cutting machine operators in the fields of milling, turning and grinding. We also train steel engravers and industrial business management assistants. Many of our apprentices stay on at Röltgen after completing their training.
Whether you are a woman, man or non-binary, we want to hear from you. Simply send your application to m.baehr@roeltgen.de.
How did the embossing technique come about?
The development of the stamping technique and its use in product labelling
The stamping technique has played an important role in labelling and individualising products for centuries. From its beginnings in ancient cultures to modern, computer-controlled stamping systems, this technique has continuously developed. Today, industrial production and product labelling would be unthinkable without the stamping technique. Find out how the technology has developed, what processes are available and how embossing technology will continue to shape the market in the future.
Introduction to embossing technology
What exactly is embossing technology? Basically, it is a method of marking or designing surfaces. This technique is used in industry primarily to permanently imprint information on a material, be it brand names, serial numbers or logos.
Origin and historical development of embossing technology
First applications and early materials
As far back as ancient times, cultures such as the Romans and Egyptians used embossing to mark coins, shields and weapons with symbols and text. During this time, simple tools and handmade stamps were used to emboss characters into metals and identify products.
The Industrial Revolution and the development of modern embossing techniques
The first major change came with the industrial revolution: machines increasingly replaced manual labour, and embossing could now be done faster and more precisely. The introduction of mechanical presses made it possible to mass-produce embossed products, which became particularly relevant for currencies, identification documents and industrial labelling.
Technological advances and their impact on embossing technology
Mechanical embossing technology and first machines
In the 19th century, embossing technology achieved a new level of precision with mechanical presses. These machines increased the repeatability and speed of the embossing process – a major advantage in the emerging world of mass production.
Electrical and digital innovations
With electrification and later digitalisation, even more precise and adaptable stamping processes were added. Today, CNC-controlled machines make it possible to produce even complex stampings at high speed and with a low error rate, making them almost indispensable for modern manufacturing.
Fields of application for stamping technology today
Stamping in metal processing
In the metal industry, stamping technology plays an important role in marking metal parts with logos, serial numbers or production data. These markings are resistant even to intensive use and high temperatures.
Application in the plastics and textile industry
Plastics can also be stamped – from components to promotional items to packaging. In the textile sector, stamping technology is used to permanently apply labels, brand logos or patterns to textiles.
Stamping technology in the automotive and aerospace industries
In the automotive and aerospace industries, stamping technology is used not only for labelling, but also for the traceability of components. This ensures that information such as production data and serial numbers can be reliably preserved even under extreme conditions.
Why stamping technology is indispensable for product labelling
Durability and resistance of stamping
A key advantage of embossing is its durability. Once embossed, the marking can withstand high temperatures, mechanical abrasion and corrosive environments.
Security and counterfeit protection through embossing
Embossing increases the security of products because it is difficult to copy or manipulate. This is an important protection against counterfeiting, especially for high-quality branded products.
The most important embossing techniques
Impact embossing and roll-on embossing
In impact embossing, the embossing tool is struck against the material with an impact – ideal for deeper and highly resistant embossing. Roll-on embossing, on the other hand, is well suited for serial productions with even embossing on round, smooth surfaces.
Deep embossing and surface embossing
Deep embossing creates permanent indentations in the material that are particularly resistant. Surface embossing, on the other hand, highlights certain areas without penetrating deeply into the material and is often used for decorative elements.
Modern stamping technology: flexibility and precision in application
Automated stamping technology for mass production
Today’s stamping technology is extremely productive thanks to automated machines. In mass production, CNC machines ensure precise, fast and repeatable stamping – ideal for large production volumes.
Customisation for customer-specific labelling
Flexibility is in demand: computer-controlled machines now allow customer-specific labelling to be applied to different products without additional set-up times. This is a decisive advantage for companies that depend on individual labelling.
Future prospects for embossing technology
Sustainable materials and energy-efficient processes
In the future, marking technology will increasingly rely on sustainable materials and energy-efficient processes. Tools made from recycled material or coatings that require less energy during the marking process are gaining in importance.
Integration of marking technology into digital production processes
With increasing digitalisation, marking systems are being integrated into intelligent production processes. This allows markings to be seamlessly integrated into the existing production line and data to be used in real time for quality management.
Conclusion
The stamping technique has a long and exciting history of development and remains indispensable in modern manufacturing. Its ability to create robust and permanent marks makes it one of the most versatile techniques for product marking. The development of new, sustainable technologies will further advance the use of stamping technology.
FAQs:
Why is the stamping technique so important for product marking?
The stamping technique offers a long-lasting and durable way to mark products. These marks will remain even under extreme conditions and are therefore ideal for industrial use.
What materials can be stamped?
The stamping technique is versatile and can be used on a wide variety of materials, including metal, plastic, leather and even textiles. However, each material requires adapted tools and techniques.
How does impact stamping differ from roller stamping?
Impact marking uses a strong impact to create a deep impression, which is ideal for robust labelling on small surfaces. Roll-on marking, on the other hand, is suitable for round, smooth surfaces and is used for uniform, repeatable imprints in series production.
What advantages does the marking technique offer compared to other labelling methods?
Markings are extremely resistant to abrasion, heat and weathering. Unlike printed or glued labels, an embossed marking remains permanently in the material and is therefore more durable and tamper-proof.
How will the stamping technique develop in the future?
The stamping technique will continue to develop in the direction of digitalisation and sustainability. Automated and energy-efficient machines, recycled materials and intelligent production processes will make the stamping technique even more flexible and environmentally friendly.

let's get connected
Do you have a question?
Benefit from our many years of experience and let us advise you personally on your individual applications.